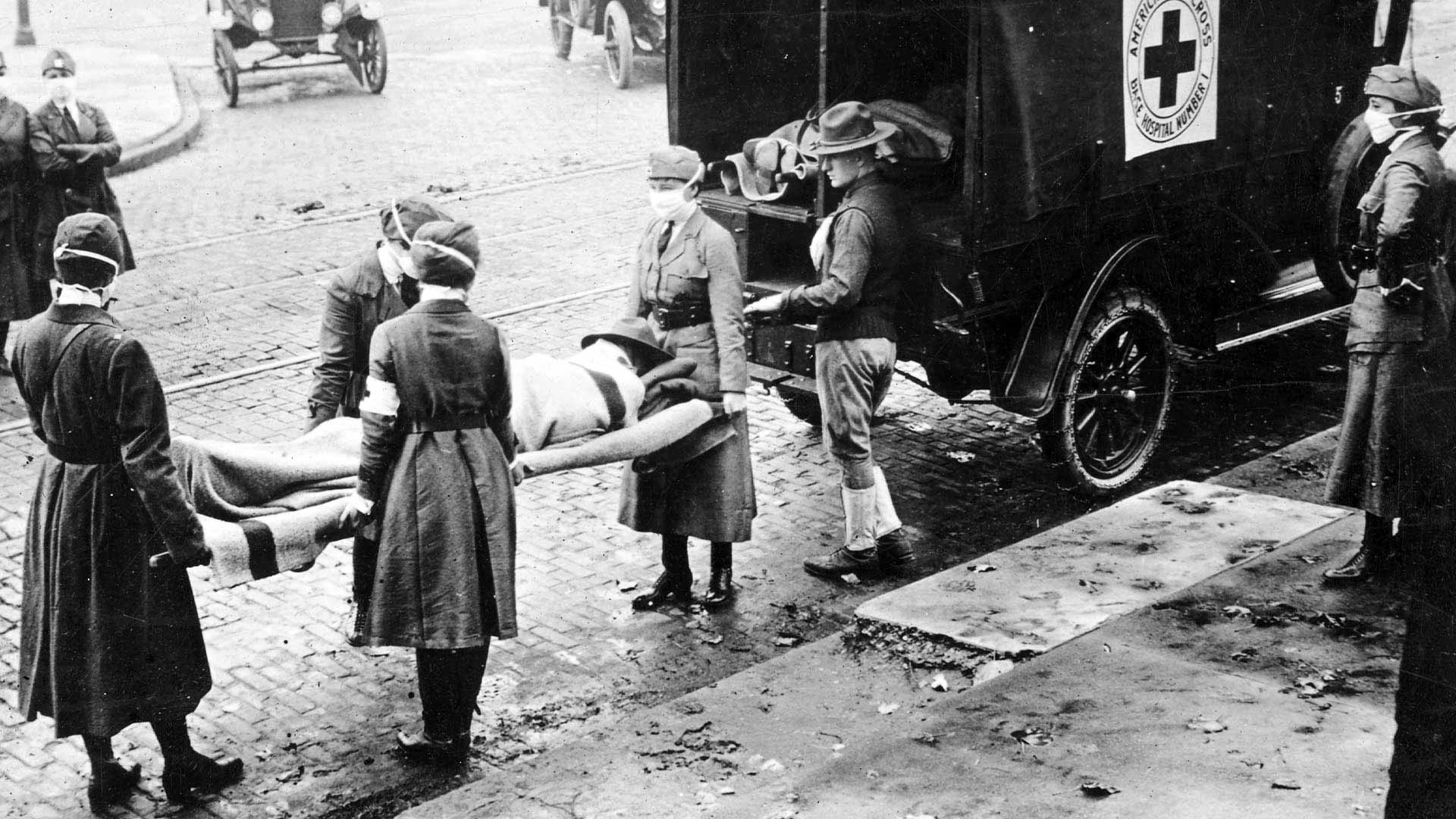
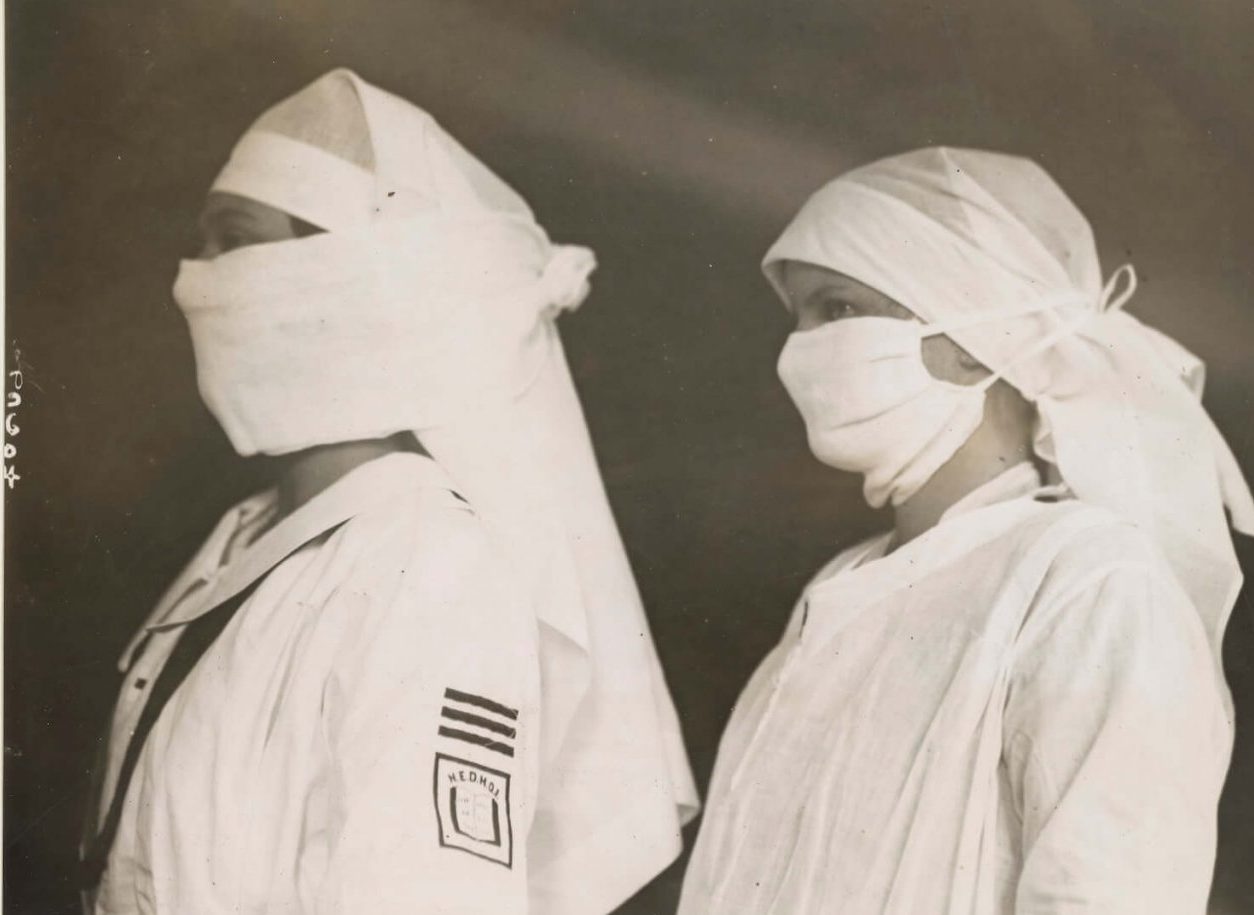
The 1918–1919 Influenza Pandemic was one of the deadliest pandemics in history, affecting hundreds of millions of people around the globe.
Occurring against the backdrop of World War I, the pandemic added to the horrors and devastation brought on by that conflict.