digital
What is digital?
Digital describes electronic technology that generates, stores and processes data in terms of positive and nonpositive states. Positive is expressed or represented by the number 1 and nonpositive by the number 0. Thus, data transmitted or stored with digital technology is expressed as a string of 0s and 1s. Each of these state digits is referred to as a bit; a string of bits that a computer can address individually as a group is a byte.
Before the digital age, electronic transmission was limited to analog technology, which conveys data as electronic signals of varying frequency or amplitude added to carrier waves of a given frequency. Broadcast and phone transmission have conventionally used analog technology.
The word digital can also, more broadly, apply to anything that's represented or processed by means of digital technology, such as virtual reality, audiobooks, digital music, mobile apps, digital art, digital communication, digital media, podcasts and digital marketing.
Communication with digital technology
Digital technology is primarily used with new physical communications media, such as satellite and fiber optic transmission. A modem is used to convert the digital information in computers to analog signals for phone lines and to convert analog phone signals to digital information for computers.
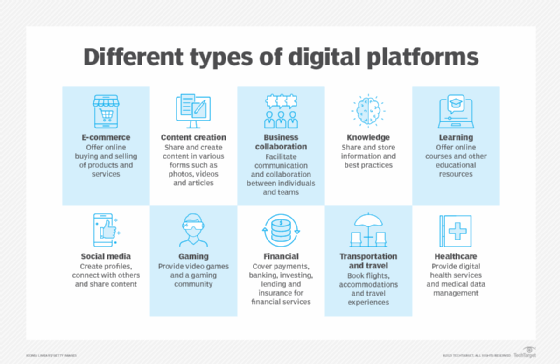
Communication through digital technology can also include a wide range of communication channels such as email, text messaging, social media marketing, video conferencing, instant messaging, e-commerce and collaboration tools.
Examples of digital technology and concepts
Digital technology, which is a key driver of recent trends in digital transformation, is revolutionizing a wide range of industries, businesses and various aspects of life.
Common examples of digital technology and concepts include the following:
- Digital and electronic devices. This is physical equipment that uses digital data. Examples of digital devices and electronics include PCs, smartphones, cameras and laptops.
- Digital signal. A digital signal is used to convey discrete values, usually expressed as binary numbers 0 and 1. In contrast to analog signals, digital signals can only take on a limited number of values and vary constantly.
- Digital media. Digital media is any sort of media content that's created, distributed and consumed using digital technology. This includes digital images, photos, music, video games and interactive features and other digital material types.
- Digital data. Digital data is information that's represented or stored in a discrete, binary format using values of 0s and 1s. This is in contrast to analog data, which is represented in a continuous, nondiscrete form.
Benefits of being digital
Embracing digital technologies lets individuals, businesses and organizations enhance their efficiency and competitiveness in a world that's progressively becoming more digital.
Common benefits of going digital include the following:
- Improved customer experience. Digital tools and technologies such as chatbots and customer relationship management systems improve customer experience and response times.
- Automation. Supply chain and business processes can be automated by using digital technologies such as machine learning, artificial intelligence and robotic process automation These digital technologies help to streamline operations, provide real-time insights and minimize manual intervention.
- Ease of accessibility and management. Digital data is easier to access and manage. For example, unlike analog data -- such as a vinyl record -- a digital recording can be copied, edited and moved without a loss of sound quality.
- Simplified storage. Digital data can be conveniently stored on hard drives, solid-state drives, memory cards and cloud storage. This makes it easy for businesses and users to track and manage large volumes of data. For example, thousands of songs can be stored on a USB key, while the same amount of music would require a room to be stored physically.
- Quick access to information. Digital platforms such as the internet and search engines make it easy to extract information on any topic.
- Enhanced flexibility. Digital technologies let people work remotely from any location in the world. Digital collaboration tools such as Zoom and Microsoft Teams let employees work from anywhere and don't require them to have designated office spaces for work.
- Versatility. Digital products can be effortlessly integrated into a business and marketing strategy at any stage of the sales funnel.
As the digital landscape evolves, the significance of digital transformation continues to rise. Review this in-depth guide to learn the fundamentals of digital transformation and see how businesses can embrace it successfully.
