Abstract
Purpose
This narrative review provides an overview of the current knowledge of B-mode ultrasound-derived echo intensity (EI) as an indicator of skeletal muscle quality.
Method
PubMed and Google Scholar were used to search the literature. Advanced search functions were used to find original studies with the terms ‘echo intensity’ and/or ‘muscle quality’ in the title and/or abstract. Publications that conceptually described muscle quality but did not include measurement of EI were not a focus of the review.
Result
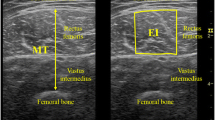
Importantly, the foundational premise of EI remains unclear. While it is likely that EI reflects intramuscular adiposity, data suggesting that these measurements are influenced by fibrous tissue is limited to diseased muscle and animal models. EI appears to show particular promise in studying muscular aging. Studies have consistently reported an association between EI and muscle function, though not all chronic interventions have demonstrated improvements. Based on the existing literature, it is unclear if EI can be used as a marker of muscle glycogen following exercise and nutritional interventions, or if EI is influenced by hydration status. Inconsistent methodological approaches used across laboratories have made comparing EI studies challenging. Image depth, rest duration, participant positioning, probe tilt, and the decision to correct for subcutaneous adipose tissue thickness are all critical considerations when interpreting the literature and planning studies.
Conclusion
While some areas show conflicting evidence, EI shows promise as a novel tool for studying muscle quality. Collaborative efforts focused on methodology are necessary to enhance the consistency and quality of the EI literature.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EI:
-
Echo intensity
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
References
Akagi R, Suzuki M, Kawaguchi E, Miyamoto N, Yamada Y, Ema R (2018) Muscle size-strength relationship including ultrasonographic echo intensity and voluntary activation level of a muscle group. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 75:185–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2017.12.012
Akazawa N, Okawa N, Tamura K, Moriyama H (2017) Relationships between intramuscular fat, muscle strength and gait independence in older women: a cross-sectional study. Geriatr Gerontol Int 17:1683–1688. https://doi.org/10.1111/ggi.12869
Akima H, Hioki M, Yoshiko A, Koike T, Sakakibara H, Takahashi H, Oshida Y (2016) Intramuscular adipose tissue determined by T1-weighted MRI at 3T primarily reflects extramyocellular lipids. Magn Reson Imaging 34:397–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2015.12.038
Arroyo E, Stout JR, Beyer KS, Church DD, Varanoske AN, Fukuda DH, Hoffman JR (2018) Effects of supine rest duration on ultrasound measures of the vastus lateralis. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 38:155–157. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpf.12403
Arts IM, Pillen S, Schelhaas HJ, Overeem S, Zwarts MJ (2010) Normal values for quantitative muscle ultrasonography in adults. Muscle Nerve 41:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.21458
Arts IM et al (2012) Intramuscular fibrous tissue determines muscle echo intensity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 45:449–450. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.22254
Bali AU, Harmon KK, Burton AM, Phan DC, Mercer NE, Lawless NW, Stock MS (2020) Muscle strength, not age, explains unique variance in echo intensity. Exp Gerontol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2020.111047
Berg HE, Tedner B, Tesch PA (1993) Changes in lower limb muscle cross-sectional area and tissue fluid volume after transition from standing to supine. Acta Physiol Scand 148:379–385. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-1716.1993.tb09573.x
Burton AM, Stock MS (2018) Consistency of novel ultrasound equations for estimating percent intramuscular fat. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpf.12532
Cadore EL et al (2012) Echo intensity is associated with skeletal muscle power and cardiovascular performance in elderly men. Exp Gerontol 47:473–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2012.04.002
Chooi YC, Ding C, Magkos F (2019) The epidemiology of obesity. Metab Clin Exp 92:6–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2018.09.005
Damas F et al (2016) Early resistance training-induced increases in muscle cross-sectional area are concomitant with edema-induced muscle swelling. Eur J Appl Physiol 116:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-015-3243-4
Dankel SJ et al (2018) The impact of ultrasound probe tilt on muscle thickness and echo-intensity: a cross-sectional study. J Clin Densitom. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocd.2018.10.003
Delmonico MJ et al (2009) Longitudinal study of muscle strength, quality, and adipose tissue infiltration. Am J Clin Nutr 90:1579–1585. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2009.28047
Dorn TW, Schache AG, Pandy MG (2012) Muscular strategy shift in human running: dependence of running speed on hip and ankle muscle performance. J Exp Biol 215:1944–1956. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.064527
Fragala MS, Kenny AM, Kuchel GA (2015) Muscle quality in aging: a multi-dimensional approach to muscle functioning with applications for treatment. Sports Med 45:641–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-015-0305-z
Fukumoto Y et al (2012) Skeletal muscle quality assessed from echo intensity is associated with muscle strength of middle-aged and elderly persons. Eur J Appl Physiol 112:1519–1525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-011-2099-5
Fukumoto Y et al (2015) Age-related ultrasound changes in muscle quantity and quality in women. Ultrasound Med Biol 41:3013–3017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2015.06.017
Fukumoto Y et al (2018) Association of physical activity with age-related changes in muscle echo intensity in older adults: a 4-year longitudinal study. J Appl Physiol (1985) 125:1468–1474. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00317.2018
Gerstner GR, Giuliani HK, Mota JA, Ryan ED (2017a) Age-related reductions in muscle quality influence the relative differences in strength and power. Exp Gerontol 99:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2017.09.009
Gerstner GR, Thompson BJ, Rosenberg JG, Sobolewski EJ, Scharville MJ, Ryan ED (2017b) Neural and muscular contributions to the age-related reductions in rapid strength. Med Sci Sports Exerc 49:1331–1339. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000001231
Goodpaster BH, Stenger VA, Boada F, McKolanis T, Davis D, Ross R, Kelley DE (2004) Skeletal muscle lipid concentration quantified by magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Clin Nutr 79:748–754. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/79.5.748
Goodpaster BH et al (2008) Effects of physical activity on strength and skeletal muscle fat infiltration in older adults: a randomized controlled trial. J Appl Physiol (1985) 105:1498–1503. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.90425.2008
Guadagnin EC, Priario LAA, Carpes FP, Vaz MA (2019) Correlation between lower limb isometric strength and muscle structure with normal and challenged gait performance in older adults. Gait Posture 73:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2019.07.131
Hill JC, Millan IS (2014) Validation of musculoskeletal ultrasound to assess and quantify muscle glycogen content. A novel approach. Phys Sportsmed 42:45–52. https://doi.org/10.3810/psm.2014.09.2075
Ikezoe T, Kobayashi T, Nakamura M, Ichihashi N (2017) Effects of low-load, higher-repetition versus high-load, lower-repetition resistance training not performed to failure on muscle strength, mass, and echo intensity in healthy young men: a time-course study. J Strength Cond Res. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000002278
Isaka M et al (2019) The usefulness of an alternative diagnostic method for Sarcopenia using thickness and echo intensity of lower leg muscles in older males. J Am Med Dir Assoc 20:1185 e1181-1185 e1188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2019.01.152
Jajtner AR et al (2013) Performance and muscle architecture comparisons between starters and nonstarters in National Collegiate Athletic Association Division I women’s soccer. J Strength Cond Res 27:2355–2365. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0b013e31829bd7c5
Jenkins ND (2016) Are resistance training-mediated decreases in ultrasound echo intensity caused by changes in muscle composition, or is there an alternative explanation? Ultrasound Med Biol 42:3050–3051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2016.07.011
Jenkins ND et al (2015) Test-retest reliability of single transverse versus panoramic ultrasound imaging for muscle size and echo intensity of the biceps brachii. Ultrasound Med Biol 41:1584–1591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2015.01.017
Jenkins NDM, Miramonti AA, Hill EC, Smith CM, Cochrane-Snyman KC, Housh TJ, Cramer JT (2017) Greater neural adaptations following high- vs low-load resistance training. Front Physiol 8:331. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00331
Katsiaras A et al (2005) Skeletal muscle fatigue, strength, and quality in the elderly: the Health ABC Study. J Appl Physiol (1985) 99:210–216. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01276.2004
Kawai H et al (2018) Morphological and qualitative characteristics of the quadriceps muscle of community-dwelling older adults based on ultrasound imaging: classification using latent class analysis. Aging Clin Exp Res 30:283–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-017-0781-0
Kleinberg CR, Ryan ED, Tweedell AJ, Barnette TJ, Wagoner CW (2016) Influence of lower extremity muscle size and quality on stair-climb performance in career firefighters. J Strength Cond Res 30:1613–1618. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000001268
Lopez P, Wilhelm EN, Rech A, Minozzo F, Radaelli R, Pinto RS (2017) Echo intensity independently predicts functionality in sedentary older men. Muscle Nerve 55:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.25168
Lopez P, Pinto MD, Pinto RS (2019) Does rest time before ultrasonography imaging affect quadriceps femoris muscle thickness, cross-sectional area and echo intensity measurements? Ultrasound Med Biol 45:612–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2018.10.010
MacLennan RJ, Sahebi M, Becker N, Davis E, Garcia JM, Stock MS (2020) Declines in skeletal muscle quality vs. size following two weeks of knee joint immobilization. PeerJ 8:e8224. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.8224
Mangine GT et al (2014) Influence of gender and muscle architecture asymmetry on jump and sprint performance. J Sports Sci Med 13:904–911
Mangine GT et al (2015) Sprinting performance on the Woodway Curve 3.0 is related to muscle architecture. Eur J Sport Sci 15:606–614. https://doi.org/10.1080/17461391.2014.969322
Mangine GT et al (2018) Resistance training does not induce uniform adaptations to quadriceps. PLoS ONE 13:e0198304. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0198304
Manini TM, Clark BC, Nalls MA, Goodpaster BH, Ploutz-Snyder LL, Harris TB (2007) Reduced physical activity increases intermuscular adipose tissue in healthy young adults. Am J Clin Nutr 85:377–384. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/85.2.377
Masaki M et al (2016) Association of walking speed with sagittal spinal alignment, muscle thickness, and echo intensity of lumbar back muscles in middle-aged and elderly women. Aging Clin Exp Res 28:429–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-015-0442-0
Matta TT, Pinto RO, Leitao BFM, Oliveira LF (2019) Non-uniformity of elbow flexors damage induced by an eccentric protocol in untrained men. J Sports Sci Med 18:223–228
McGregor RA, Cameron-Smith D, Poppitt SD (2014) It is not just muscle mass: a review of muscle quality, composition and metabolism during ageing as determinants of muscle function and mobility in later life. Longev Healthspan 3:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-2395-3-9
McKay BD, Yeo NM, Jenkins NDM, Miramonti AA, Cramer JT (2017) Exertional rhabdomyolysis in a 21-year-old healthy woman: a case report. J Strength Cond Res 31:1403–1410. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000001824
Melvin MN, Smith-Ryan AE, Wingfield HL, Fultz SN, Roelofs EJ (2014a) Evaluation of muscle quality reliability and racial differences in body composition of overweight individuals. Ultrasound Med Biol 40:1973–1979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2014.03.012
Melvin MN, Smith-Ryan AE, Wingfield HL, Ryan ED, Trexler ET, Roelofs EJ (2014b) Muscle characteristics and body composition of NCAA division I football players. J Strength Cond Res 28:3320–3329. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000000651
Miller JD, Herda TJ, Trevino MA, Sterczala AJ, Ciccone AB, Nicoll JX (2017) Age-related differences in twitch properties and muscle activation of the first dorsal interosseous. Clin Neurophysiol 128:925–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2017.03.032
Miron Mombiela R, Facal de Castro F, Moreno P, Borras C (2017) Ultrasonic echo intensity as a new noninvasive in vivo biomarker of frailty. J Am Geriatr Soc 65:2685–2690. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.15002
Mota JA, Stock MS (2017) Rectus femoris echo intensity correlates with muscle strength, but not endurance, in younger and older men. Ultrasound Med Biol 43:1651–1657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2017.04.010
Mota JA, Stock MS, Thompson BJ (2017) Vastus lateralis and rectus femoris echo intensity fail to reflect knee extensor specific tension in middle-school boys. Physiol Meas 38:1529–1541. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6579/aa791a
Mota JA, Giuliani HK, Gerstner GR, Ryan ED (2018) The rate of velocity development associates with muscle echo intensity, but not muscle cross-sectional area in older men. Aging Clin Exp Res 30:861–865. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-017-0829-1
Nieman DC, Shanely RA, Zwetsloot KA, Meaney MP, Farris GE (2015) Ultrasonic assessment of exercise-induced change in skeletal muscle glycogen content. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil 7:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13102-015-0003-z
Oranchuk DJ, Stock MS, Nelson AR, Storey AG, Cronin JB (2020) Variability of regional quadriceps echo intensity in active young men with and without subcutaneous fat correction. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab = Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme 45:745–752. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2019-0601
Osawa Y et al (2017) Relationships of muscle echo intensity with walking ability and physical activity in the very old population. J Aging Phys Activ 25:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1123/japa.2015-0203
Palmer TB, Thompson BJ (2017) Influence of age on passive stiffness and size, quality, and strength characteristics. Muscle Nerve 55:305–315. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.25231
Palmer TB, Akehi K, Thiele RM, Smith DB, Thompson BJ (2015) Reliability of panoramic ultrasound imaging in simultaneously examining muscle size and quality of the hamstring muscles in young, healthy males and females. Ultrasound Med Biol 41:675–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2014.10.011
Paris MT, Bell KE, Avrutin E, Mourtzakis M (2020) Ultrasound image resolution influences analysis of skeletal muscle composition. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 40:277–283. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpf.12636
Pillen S, Arts IM, Zwarts MJ (2008) Muscle ultrasound in neuromuscular disorders. Muscle Nerve 37:679–693. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.21015
Pillen S et al (2009) Skeletal muscle ultrasound: correlation between fibrous tissue and echo intensity. Ultrasound Med Biol 35:443–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2008.09.016
Radaelli R et al (2013) Low- and high-volume strength training induces similar neuromuscular improvements in muscle quality in elderly women. Exp Gerontol 48:710–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2013.04.003
Rech A, Radaelli R, Goltz FR, da Rosa LH, Schneider CD, Pinto RS (2014) Echo intensity is negatively associated with functional capacity in older women. Age 36:9708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-014-9708-2
Rosenberg JG, Ryan ED, Sobolewski EJ, Scharville MJ, Thompson BJ, King GE (2014) Reliability of panoramic ultrasound imaging to simultaneously examine muscle size and quality of the medial gastrocnemius. Muscle Nerve 49:736–740. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.24061
Routledge HE, Bradley WJ, Shepherd SO, Cocks M, Erskine RM, Close GL, Morton JP (2019) Ultrasound does not detect acute changes in glycogen in vastus lateralis of man. Med Sci Sports Exerc 51:2286–2293. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000002052
Russ DW, Gregg-Cornell K, Conaway MJ, Clark BC (2012) Evolving concepts on the age-related changes in “muscle quality.” J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 3:95–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13539-011-0054-2
Ryan ED, Shea NW, Gerstner GR, Barnette TJ, Tweedell AJ, Kleinberg CR (2016) The influence of subcutaneous fat on the relationship between body composition and ultrasound-derived muscle quality. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab = Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme 41:1104–1107. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2016-0238
Sarvazyan A, Tatarinov A, Sarvazyan N (2005) Ultrasonic assessment of tissue hydration status. Ultrasonics 43:661–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2005.03.005
Scanlon TC, Fragala MS, Stout JR, Emerson NS, Beyer KS, Oliveira LP, Hoffman JR (2014) Muscle architecture and strength: adaptations to short-term resistance training in older adults. Muscle Nerve 49:584–592. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.23969
Shea NW (2017) Effects of acute supine rest and hydration status on mid-thigh muscle size and quality as measured by ultrasonography. (Doctoral dissertation). https://cdr.lib.unc.edu/concern/parent/9w0323552/file_sets/bz0323560cw0323583x. Accessed 7 June 2020
Stock MS et al (2017a) The time course of short-term hypertrophy in the absence of eccentric muscle damage. Eur J Appl Physiol 117:989–1004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3587-z
Stock MS, Mota JA, Hernandez JM, Thompson BJ (2017b) Echo intensity and muscle thickness as predictors of athleticism and isometric strength in middle-school boys. Muscle Nerve 55:685–692. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.25395
Stock MS, Whitson M, Burton AM, Dawson NT, Sobolewski EJ, Thompson BJ (2018) Echo intensity versus muscle function correlations in older adults are influenced by subcutaneous fat thickness. Ultrasound Med Biol 44:1597–1605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2018.04.009
Stock MS, Oranchuk DJ, Burton AM, Phan DC (2020) Age, sex, and region-specific differences in skeletal muscle size and quality. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab = Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2020-0114
Strasser EM, Draskovits T, Praschak M, Quittan M, Graf A (2013) Association between ultrasound measurements of muscle thickness, pennation angle, echogenicity and skeletal muscle strength in the elderly. Age 35:2377–2388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-013-9517-z
Tait RG Jr (2016) Ultrasound use for body composition and carcass quality assessment in cattle and lambs. Vet Clin N Am Food Anim Pract 32:207–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvfa.2015.09.007
Tanaka NI, Ogawa M, Yoshiko A, Ando R, Akima H (2017) Reliability of size and echo intensity of abdominal skeletal muscles using extended field-of-view ultrasound imaging. Eur J Appl Physiol 117:2263–2270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3713-y
Taniguchi M et al (2017) Increase in echo intensity and extracellular-to-intracellular water ratio is independently associated with muscle weakness in elderly women. Eur J Appl Physiol 117:2001–2007. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3686-x
Tomko PM, Muddle TW, Magrini MA, Colquhoun RJ, Luera MJ, Jenkins ND (2018) Reliability and differences in quadriceps femoris muscle morphology using ultrasonography: the effects of body position and rest time. Ultrasound 26:214–221. https://doi.org/10.1177/1742271X18780127
Trexler ET, Smith-Ryan AE, Roelofs EJ, Hirsch KR (2015) Body composition, muscle quality and scoliosis in female collegiate gymnasts: a pilot study. Int J Sports Med 36:1087–1092. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1555781
Vakula MN, Fisher KL, Garcia SA, Holmes SC, Post BK, Costa PB, Pamukoff DN (2019) Quadriceps impairment is associated with gait mechanics in young adults with obesity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 51:951–961. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000001891
Varanoske AN et al (2019) Effects of rest position on morphology of the vastus lateralis and its relationship with lower-body strength and power. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol 4:64
Varanoske AN, Coker NA, Johnson BD, Belity T, Wells AJ (2020) Influence of muscle depth and thickness on ultrasound echo intensity of the vastus lateralis. Acta Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185120958405
Watanabe Y et al (2013) Echo intensity obtained from ultrasonography images reflecting muscle strength in elderly men. Clin Interv Aging 8:993–998. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S47263
Watanabe Y, Ikenaga M, Yoshimura E, Yamada Y, Kimura M (2018) Association between echo intensity and attenuation of skeletal muscle in young and older adults: a comparison between ultrasonography and computed tomography. Clin Interv Aging 13:1871–1878
Wearing J, Stokes M, de Bruin ED (2019) Quadriceps muscle strength is a discriminant predictor of dependence in daily activities in nursing home residents. PLoS ONE 14:e0223016. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0223016
Wilhelm EN et al (2014a) Concurrent strength and endurance training exercise sequence does not affect neuromuscular adaptations in older men. Exp Gerontol 60:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2014.11.007
Wilhelm EN, Rech A, Minozzo F, Radaelli R, Botton CE, Pinto RS (2014b) Relationship between quadriceps femoris echo intensity, muscle power, and functional capacity of older men. Age 36:9625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-014-9625-4
Wilkinson TJ, Gould DW, Nixon DGD, Watson EL, Smith AC (2019) Quality over quantity? Association of skeletal muscle myosteatosis and myofibrosis on physical function in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 34:1344–1353. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfy139
Wong V, Spitz RW, Bell ZW, Viana RB, Chatakondi RN, Abe T, Loenneke JP (2020) Exercise induced changes in echo intensity within the muscle: a brief review. J Ultrasound. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-019-00424-y
Yamada M et al (2017) Differential characteristics of skeletal muscle in community-dwelling older adults. J Am Med Dir Assoc 18:807 e809-807 e816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2017.05.011
Yitzchaki N, Kuehne TE, Mouser JG, Buckner SL (2019) Can changes in echo intensity be used to detect the presence of acute muscle swelling? Physiol Meas 40:045002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6579/ab122a
Yitzchaki N, Zhu WG, Kuehne TE, Vasenina E, Dankel SJ, Buckner SL (2020) An examination of changes in skeletal muscle thickness, echo intensity, strength and soreness following resistance exercise. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 40:238–244. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpf.12630
Yoshiko A, Kaji T, Sugiyama H, Koike T, Oshida Y, Akima H (2018a) Muscle quality characteristics of muscles in the thigh, upper arm and lower back in elderly men and women. Eur J Appl Physiol 118:1385–1395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-3870-7
Yoshiko A et al (2018b) Effects of 10-week walking and walking with home-based resistance training on muscle quality, muscle size, and physical functional tests in healthy older individuals. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act 15:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11556-018-0201-2
Yoshiko A et al (2019) Higher and lower muscle echo intensity in elderly individuals is distinguished by muscle size, physical performance and daily physical activity. Ultrasound Med Biol 45:2372–2380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2019.05.029
Young HJ, Jenkins NT, Zhao Q, McCully KK (2015) Measurement of intramuscular fat by muscle echo intensity. Muscle Nerve 52:963–971. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.24656
Young HJ, Southern WM, McCully KK (2016) Comparisons of ultrasound-estimated intramuscular fat with fitness and health indicators. Muscle Nerve 54:743–749. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.25105
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors contributed equally to all aspects of this review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in the reporting of this research.
Additional information
Communicated by Michael Lindinger.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stock, M.S., Thompson, B.J. Echo intensity as an indicator of skeletal muscle quality: applications, methodology, and future directions. Eur J Appl Physiol 121, 369–380 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-020-04556-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-020-04556-6